 THE MAIN ASPECTS OF CHOOSING THE ENTERPRISES' OPERATING
STRATEGY
THE MAIN ASPECTS OF CHOOSING THE ENTERPRISES' OPERATING
STRATEGY
Yuliia Karpenko
Odesa National Economic University, Ukraine
E-mail:
juliakarpenko50@gmail.com
Anzhelika Pienova
Odesa National Economic University, Ukraine
E-mail: a_penova2015@ukr.net
Dmytro Melnychuk
Zhytomyr Polytechnic State
University, Ukraine
E-mail: melndp@ukr.net
Valentyna Kutsyk
Lviv University of Trade and Economics, Ukraine
E-mail: valentynakutsyk@gmail.com
Nataliya Nakonechna
Lviv State University of Internal Affairs, Ukraine
E-mail: nakonnat@gmail.com
Sergiy Kalinichenko
Kharkiv Petro Vasilenko National Technical University
of Agriculture, Ukraine
E-mail:
kalinichenko.sergiy@gmail.com
Submission:
8/8/2021
Revision: 9/13/2021
Accept: 9/22/2021
ABSTRACT
Retail trade occupies an important place in the economy of Ukraine,
ensuring the sale of manufactured goods to end consumers. For retailers, it is
important to achieve timeliness and reliability of services to meet customer
needs, which can be achieved through the formation of operational strategy. The
purpose of the article is to form a methodological approach to the development
of operational strategy of retail enterprises, which is based on the
requirements of corporate strategy, selected in accordance with the stage of
the life cycle of the industry. The development of this methodological approach
was carried out on the basis of Hill's
model and system approach. As a result, a logical scheme of the process of developing
an operational strategy is presented, which is specified by the list of input and
output information. In order to
determine the stage of the life cycle of the market of retail services in
Ukraine, the eponymous concept of Porter was applied and the analysis was
carried out according to the criteria: consumers and their behaviour, sales costs, changes
in services, the nature of competition, profitability and found that the retail
services market is growing. The
method of observation, comparative and analytical method was used for the analysis,
the Herfindahl-Hirschman index (HHI) was calculated on the basis of the data
of the largest retail trade enterprises of Ukraine. As a result, it was found
that the market of retail services in Ukraine is growing. With this in mind, an
operational strategy for Ukrainian retailers has been proposed, which should
aim to ensure the flexibility and variability of the operating system. The
defined general direction of the operational strategy will allow to establish
the content of decisions on the choice of operational processes, as well as the
infrastructure to support them.
Keywords: operational
strategy; industry life cycle; retail enterprises of
Ukraine; operational processes
1.
INTRODUCTION
As an important component of
Ukraine’s economy, retail is one of the five most profitable industries and
provides jobs for one in seven employees. High profits and low barriers to
entry attract entrepreneurs, so the intensity of competition is growing every
year. In such conditions, retailers are trying to achieve sustainable
competitive advantages and are increasingly paying attention to operations as
one of the sources of their formation.
In modern business
conditions, one of the sources of competitive advantages of the enterprise may
be operations. Successful implementation of operations that form the main
operational function of the enterprise, as well as the latter's focus on
achieving a certain operational priority, including low production costs, high
quality and reliability of products, fast order fulfilment, high reliability of
supply, ability to respond to changes in demand, flexibility and speed
development of new products, increases the attractiveness of the enterprise
compared to competitors.
An
effective operational strategy is needed to form and maintain an enterprise's
operational priority, but its development is often underestimated by
management. In addition, scientific research does not provide recommendations
for the choice of operational strategy taking into account the main aspects of
the life of the trade
enterprises, in particular the stage of the life cycle of
the industry in which they
work.
2.
LITERATURE REVIEW
The content of
operational strategies, classification approaches to them, the main stages of
development, as well as the importance of operational strategies in the
development of supply chain, coordination with financial, information and
corporate strategies, the formation of operational strategies by enterprises of
various fields of activity, set out in the scientific works of a number of
scientists: Chapman and Gatewood (2017), Chase, Jacobs and Aquilano
(2019), Wang and Huang (2019), Santa et al. (2020), Tarigan
and Siagan (2021), Zatta et
al. (2021), Ishfaq and Raja (2020) and Zhang, Zhang
and Yue (2021).
One of the first scientists
to pay attention to the formation of operational strategy was a famous
scientist Hill (2005), who researched and outlined the main stages of its
development.
The focus of the
operational strategy to meet market needs is emphasized by Chapman et al. (2017).
Scientists have examined in detail the main operational decisions for inventory
management of the enterprise.
A comprehensive study
of theoretical and practical aspects of operational management, the main types
of operational decisions was conducted by scientists Chase, Jacobs, Aquilano (2019).
Researchers (Wang &
Huang, 2019) consider the importance of operational strategies and their
integration with financial strategies in the development of a flexible supply
chain with limited capital. The authors' work confirms that joint decisions of
operational and financial strategies will be able to improve the flexibility of
the supply chain and its performance in extreme situations.
The effect of
coordination between operational, informational and corporate strategies has
been studied in the scientific work of scientists (Santa et al., 2020). The
analysis surveyed 138 large utility companies in the Australian electricity
sector, and as a result used modelling using structural equations to establish
the relationship between variables. As a result, the authors found that
coordinating operational and information strategies can improve the efficiency
of companies.
The impact of strategic
planning on the operating activities of the enterprise is analysed by the
authors (Tarigan & Siagan,
2021). Researchers note that procurement strategy and strategic partnership
mediate the impact of strategic planning on operational results.
The scientific work of
scientists (Zatta et al., 2021) is devoted to the
study of the relationship between operational strategy and supply chain
management. In particular, the study discusses the impact of relational
resources on the performance of purchasing companies. The results show that
operational skills are developed as a result of the interaction of relational
resources shared in the supply chain.
Scientific sources also
include research by the authors on the formation of operational strategies in
the field of services. Thus, the means of solving operational problems in the
field of trade are studied in the achievements of scientists (Ishfaq & Raja, 2020). In particular, to address issues
related to the inaccuracy of records regarding stocks in retail stores,
scientists have proposed to conduct a technological audit of stocks and prove
the effectiveness of this tool compared to others.
Researchers
(Zhang; Zhang & Yue, 2021) proposed an operational strategy for retail
companies that are not exposed to risk, including coordinated pricing and
replenishment of retail stocks in a competitive environment.
A review of scientific sources on the formation of operational strategy
leads to the conclusion that, despite the existing scientific developments in
this area, requires a detailed approach to developing operational strategy of
the enterprise, taking into account the requirements of corporate strategy
defined according to the life cycle stage.
The purpose of the article is to form a methodological approach to
the development of operational strategy of the enterprise, which is based on
the requirements of corporate strategy, selected in accordance with the stage
of the life cycle of the industry.
3.
METHODOLOGY
The authors used a systematic approach and the classical
model of formation of T. Hill's operational strategy to
determine the methodological aspects of developing the operational strategy of
retail enterprises of Ukraine.
This classical model emphasizes the
subordination of corporate strategy. The concept of the
life cycle of M. Porter's industry was used to
determine the general features of the corporate strategy of retail enterprises
in Ukraine. The study of the market of retail trade services in Ukraine was
conducted using the method of observation and comparative analytical methods.
To establish the
nature of competition in the retail market of Ukraine, the level of its
concentration is determined by quantity (estimated by the Herfindahl-Hirschman
market concentration index) and qualitative characteristics: the nature of
services, market entry conditions, the presence of non-price competition.
Fifteen of the largest retail trade enterprises in Ukraine were selected as the
basis of the study.
Information for
analysis was collected through our own research, publications by Ukrainian and
foreign authors, websites of the enterprises and official statistics.
4.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
4.1.
Result: a methodological approach to
the development of operational strategy of the enterprise based on the
corporate strategy selected in accordance with the stage of the life cycle of
the industry is proposed
One of the main theses
that create the basis for the construction of the process of forming an
operational strategy is its definition, provided by well-known scientists
Chase, Jacobs and Aquilano (2019). Under the
operational strategy is proposed to understand the development of general
policies and plans for the use of enterprise resources aimed at effectively
supporting its long-term strategy. Thus, scientists emphasize the relationship
between operational and corporate strategy, and for service organizations
emphasize the inseparability of operational strategy from corporate.
The subordination of
the operational strategy to the overall strategy of enterprise development is
emphasized by the authors Chapman et al. (2017). Scholars note the
inevitability of conflicts between the goals of the enterprise and the goals of
marketing, finance and production. In their opinion, the operational strategy
should be balanced, i.e. to maintain customer service at the required level and
ensure the rational use of enterprise resources. Scientists also distinguish
five main levels in the system of production planning and control, the first of
which is the development of a strategic plan, and the second – the formation of
a production plan, i.e. once again emphasize the relationship between
operational and corporate strategy.
The
relationship between the basic strategic alternatives identified by the
analysis of the internal and external environment of the enterprise, and
functional strategies of the enterprise is emphasized in the source (Kotsko,
2016).
Thus, scientists are
unanimous about the statement about the relationship and subordination of
operational and enterprise development strategy.
Opinions of scientists
are somewhat divided on the main stages of formation of the operational
strategy of the enterprise. We have systematized the main stages of formation
of operational strategy, presented in the scientific works of researchers
(Kotsko, 2016; Bilyavsky, 2015; Pisareva,
2015; Chase, 2019), namely: the formation of general goals and performance
indicators of the enterprise and their approval; analysis of the external
environment of the enterprise; analysis of internal potential and formation of
operational priorities of the enterprise; choice of operational strategy
(construction of operational process; formation of infrastructure);
implementation of operational strategy; evaluation and control of operational
strategy.
In our opinion, it would be more
expedient to take as a basis the classical model of formation of T. Hill's
operational strategy (Hill, 2005). According to it, the stages of developing an
operational strategy should include:
·
setting corporate goals;
·
definition of marketing strategy to achieve goals;
·
analysis of opportunities to receive orders in
comparison with competitors;
·
development of the most appropriate processes for the
production of products or services and the selection of optimal processes;
·
definition of infrastructure to support selected
operational processes.
T. Hill's model is
sufficiently correlated with the procedure of harmonization of market
requirements and capabilities of the operational function of the Platts-Gregory
enterprise (Platts & Gregory, 1990), which is carried out in three steps:
·
study of threats and opportunities of the external
environment. At this stage, the available operating resources of the enterprise
and the achieved operational indicators are compared with market requirements;
·
analysis of methods and capabilities of the enterprise
to assess their ability to meet market requirements;
·
consideration of alternatives and development of new
operational strategies to address the shortcomings identified in the first two
stages.
·
Let's try to agree and detail the works of famous
authors.
The study of the
content of the first stage of the proposed model allows us to emphasize that
the process of forming an operational strategy is impossible without the
development of corporate strategy. It is necessary to determine the stage of
the life cycle of the industry to form a corporate strategy (Karpenko et al.,
2021). Depending on the stage of the life cycle of the industry (introduction,
growth, maturity or decline); certain changes take place in it, in particular
in sales volumes, consumer behaviour, marketing activities, state of
production, etc. The corporate strategy chosen in accordance with the stage of
the life cycle will determine the characteristics of functional strategies, in
particular operational.
At different stages of
the life cycle of the industry, marketing tasks are different. Thus, at the
stage of implementation, which is characterized by a small number of competitors
and a low percentage of consumption of goods by buyers, the main task of
marketing is to create initial demand for the product. At the stage of growth,
when new players begin to enter the market, and the percentage of consumption
of the product gradually reaches its maximum, the task of marketing is to
adequately plan future demand and maximize market share. At the stage of
growth, when new players begin to enter the market, and the percentage of
consumption of the product gradually reaches its maximum, the task of marketing
is adequate planning of long-term demand and maximizing market share. At the
stage of recession, characterized by a decrease in sales dynamics, the task of
marketing is to maintain the loyalty of existing customers.
Taking into account the
above marketing tasks, which determine the essence of the marketing strategy,
the operational priorities of the enterprise are set. They allow you to focus
on those of them that favourably distinguish the company in a competitive
environment. These priorities are formed as a result of the analysis of threats
and opportunities of the external environment and tend to change over time. The
implications of choosing each of the priorities should also be assessed.
Current operational
priorities become mandatory for operations. To achieve them, it is necessary to
assess the operational capabilities of the enterprise and compare them with
market requirements and the capabilities of competitors. If the company's
operational capabilities are sufficient to meet consumer demands, as well as
exceed the capabilities of competitors, it receives the order, and management
makes appropriate decisions about operational processes and infrastructure to
support them. In case of insufficient operational capabilities, the management
considers alternatives and takes measures to eliminate shortcomings.
In accordance with the
objectives of the marketing strategy, the operational strategy at the stage of
implementation should focus on the production of basic goods, trying to optimize
production costs. At the stage of growth, it is aimed at ensuring the
variability of production and output of improved goods of guaranteed quality,
as well as the organization and improvement of service. The stage of maturity
requires the operational strategy to create and maintain a sufficient variety
of products (emergence of new models, design improvements, etc.), which will
allow the company to maintain consumer interest in the company's products and
maintain its market share. At the stage of recession, the operating strategy is
aimed at ensuring the production of a narrow range of products under strict
control of production costs.
Also at this stage,
management may decide to implement certain types of operating strategy,
classified according to the focus on achieving a certain operational priority
or depending on the response of the operating system to changes in demand.
Thus, the strategy of low costs, quality assurance and reliability of products,
speed of order fulfilment, etc. can be implemented according to the selected
operational priority. To establish the forms of the system's response to
changes in demand, an operational strategy of matching demand can be chosen
(characterized by production in strict accordance with market needs, maintenance
of excess capacity or introduction of overtime work and involvement of
temporary staff during peak hours); equalization of production (characterized
by the same intensity of use of enterprise resources); subcontracting
(characterized by the purchase of components from external sources or
deliberate rejection of additional demand), a hybrid strategy.
The operational
strategy formed in this way is approved by the management.
Thus, the process of
forming an
operational strategy can be graphically represented by a logical scheme (Figure
1).
4.1.
Result: the stage of the life cycle
of the market of trade services is determined retail trade turnover of Ukraine;
an operational strategy for trade enterprises is proposed
In order to analyse the
life cycle of the industry, we consider it appropriate to use the eponymous
concept of Porter (2005).
The analysis will be
conducted according to the criteria: consumers and their behaviour, sales
costs, changes in services, profitability and the nature of competition.
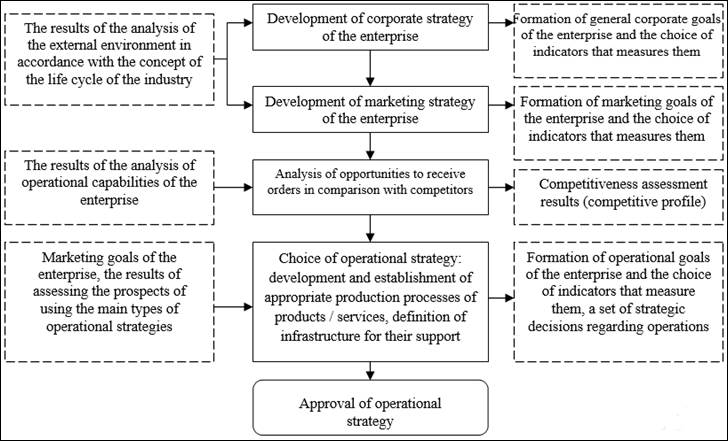
Figure 1: Logical diagram of the process of forming an
operational strategy, refined by the list of input and output information
Consumers and their behaviour. Consumer
behaviour can be investigated using the dynamics of retail trade turnover of Ukraine (Figure 2).
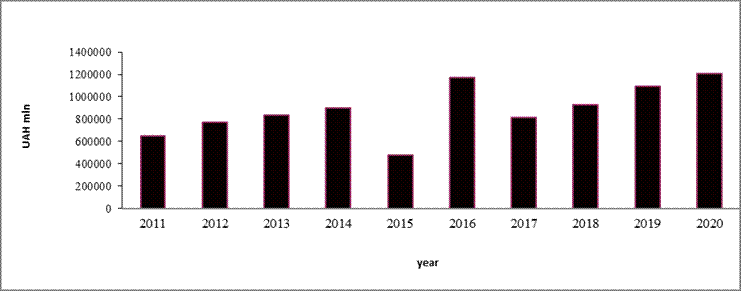
Figure 2:
Dynamics of retail trade turnover in Ukraine, UAH million
Source: built by the authors according to the
State Statistics Committee of Ukraine, 2021
It should be noted the
tendency to increase the volume of goods sold. Thus, in 2011-2020 the volume of
retail trade in general increased 1.9 times.
Selling expenses. According to a study of the financial statements of the
fifteen largest retail trade enterprises in Ukraine, their sales costs
increased by an average of 11% Analysing the
sales costs of 15 retail enterprises in Ukraine, we can conclude that the
largest retail chains increased sales costs by an average of 19% (Table 1).
Table 1: Sales costs of fifteen largest retail
enterprises in Ukraine
|
Name of Company
|
% to full cost
|
Absolute deviation 2018/2020
|
|
2018
|
2019
|
2020
|
|
LLC “ATB-MARKET”
|
16.8
|
20.6
|
20.4
|
3.6
|
|
LLC “Silpo-Fud”
|
25.5
|
27.3
|
32.9
|
7.4
|
|
LLC “FOR A”
|
24.9
|
24.7
|
28.6
|
3.7
|
|
LLC “Metro Cash & Carry Ukraine”
|
11.5
|
11.8
|
15.3
|
3.8
|
|
LLC “RUSH”
|
21
|
18.1
|
18.7
|
-2.3
|
|
LLC “Omeha”
|
14.4
|
13.6
|
14.1
|
-0.3
|
|
Others
|
18.7
|
19.2
|
21.6
|
2.9
|
Source: Data from own research (2021)
Changes in services. The results of our own research on changes in the
services of the fifteen largest retailers in Ukraine show that today there is an expansion and improvement of services of
retail trade enterprises, namely the sale of goods through online stores;
emergence of new delivery services; possibility to track the order; use of
self-service cash registers; appearance of non-cash payment terminals at
checkouts in stores with a payment function using a QR-code, which allow
contactless payment for purchases; payment through mobile applications; use of
social networks to advertise your own brand (table 2). All this indicates in
favour of expanding the range of services of retail businesses.
Table 2: Information on the expansion of services of the fifteen
largestretail trade enterprises of Ukraine
|
Services
|
Number of enterprises providing advanced services
|
|
absolute
|
relative, in% of the total number of respondents
|
|
Sale of goods through online stores
|
13
|
86.6
|
|
New delivery services
|
10
|
66.6
|
|
Ability to track orders
|
7
|
46.6
|
|
Use of self-service checkouts
|
7
|
46.6
|
|
The emergence of non-cash
payment terminals at checkouts with the function of payment by QR-code
|
15
|
100
|
|
Payment via mobile
applications
|
12
|
80
|
|
Advertising your own brand
through social networks
|
15
|
100
|
Source: Data of own
research (2021)
Profitability. To determine the level of profitability of retailers
in Ukraine, it is advisable to analyse the dynamics of their financial results
(Table 3).
Analysing the financial
results of enterprises, we can say that in general the level of market profitability
is quite high. This confirms the trend of increasing the number of profitable
enterprises and reducing unprofitable throughout the study period.
Table 3: Financial results до
оподаткування
retail trade enterprises of Ukraine
|
Years
|
Financial result before tax, UAH million
|
Profitable enterprises
|
Підприємства,
які
одержали
збиток
|
|
in% to the total number of enterprises
|
financial result, UAH million
|
in% to the total number of enterprises
|
financial result, UAH million
|
|
2011
|
21591.5
|
66.7
|
48487.9
|
33.3
|
26896.4
|
|
2012
|
9608.0
|
66.0
|
43877.8
|
34.0
|
34269.8
|
|
2013
|
-6047.6
|
67.2
|
36528.5
|
32.8
|
42576.0
|
|
2014
|
-128134.8
|
66.7
|
34360.9
|
33.3
|
162495.7
|
|
2015
|
-80564.3
|
76.1
|
56898.4
|
23.9
|
137462.7
|
|
2016
|
7277.0
|
75.8
|
74418.1
|
24.2
|
67141.1
|
|
2017
|
39296.3
|
75.2
|
89285.4
|
24.8
|
49989.1
|
|
2018
|
86290.5
|
77.2
|
116641.6
|
22.8
|
30351.1
|
|
2019
|
129113.3
|
77.1
|
159827.3
|
22.9
|
30714.0
|
|
2020
|
41896.5
|
74.4
|
121242.9
|
25.6
|
79346.4
|
Source: Research data
(2021)
In 2011, the share of
enterprises that made a profit was 66.7% of the total number of enterprises,
and in 2020 it increased to 74,4 %.
The nature of competition. According to our research,
it should be noted that there is an increase in the number and expansion of the network of
retail trade enterprises. Thus, in the first 6 months of 2020, 340 objects
were opened in Ukraine by food trade networks. In addition, in the first half
of 2020, the dynamics of opening new outlets exceeded the level of 2019 by 40%.
In general, following the results of the first half of 2020, the dynamics of
the market reached the highest level in the last ten years in terms of the
number of new outlets opened.
To determine whether
there are structuring trends in the market, we consider it necessary by
analysing the state of the retail services market in accordance with the
quantitative and qualitative signs of market concentration.
The
level of market concentration on a quantitative basis will be conducted using
the Herfindahl-Hirschman market concentration index (NIS).
The
Herfindahl-Hirschman index is calculated by the formula:
HHI = 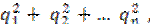 (1)
(1)
where
q is the market share of enterprises
in total, %;
n is the number of market enterprises. 9 – 9
The higher the value of
the Herfindahl-Hirschman index, the higher the level of market concentration:
·
the range from 800 to 1800 indicates
a moderate level of market concentration;
·
a range of less than 800 indicates
low market concentration;
·
a range greater than 1800 indicates
that the market is highly concentrated.
The calculation of the Herfindahl-Hirschman index (HHI) for enterprises
of the Ukrainian retail services market is presented in Table 4.
Table 4:
Calculation of the Herfindahl-Hirschman Index (HHI) for Ukrainian retail services
market enterprises
|
Enterprise
|
Market share (q), %
|
|
|
|
2018
|
2019
|
2020
|
2018
|
2019
|
2020
|
|
LLC “ATB-MARKET”
|
9.21
|
9,59
|
10.23
|
84.87
|
91.96
|
104.66
|
|
LLC “Silpo-Fud”
|
6.13
|
5.98
|
5.32
|
37.54
|
35.79
|
28.29
|
|
LLC “Epicenter K”
|
4.46
|
4.18
|
4.16
|
19.85
|
17.44
|
17.32
|
|
LLC “Metro Cash & Carry Ukraine”
|
1.87
|
1.81
|
1.77
|
3.50
|
3.27
|
3.14
|
|
LLC “FORA”
|
1.24
|
1.30
|
1.35
|
1.54
|
1.70
|
1.83
|
|
LLC “Auchan Ukraine Hypermarke”t
|
1.66
|
1.30
|
1.17
|
2.76
|
1.68
|
1.36
|
|
LLC “COMFI Trade”
|
1.31
|
1.25
|
1.34
|
1.71
|
1.55
|
1.78
|
|
LLC “Foktsroth”
|
1.31
|
1.20
|
1.18
|
1.72
|
1.43
|
1.40
|
|
PE “Eva”
|
1.08
|
1.18
|
1.11
|
1.17
|
1.38
|
1.23
|
|
PE “Rozetka”
|
0.92
|
1.11
|
1.49
|
0.84
|
1.24
|
2.22
|
|
PE “Varus”
|
1.13
|
1.03
|
0.94
|
1.29
|
1.07
|
0.89
|
|
LLC “Kviza-Treyd”
|
0.99
|
1.01
|
0.97
|
0.98
|
1.02
|
0.95
|
|
LLC “Novus
Ukrayina”
|
0.98
|
1.00
|
0.92
|
0.96
|
1.00
|
0.84
|
|
PE
“Eldorado”
|
1.04
|
0.88
|
0.94
|
1.09
|
0.78
|
0.89
|
|
LLC “Fozzi-Fud”
|
0.87
|
0.79
|
0.73
|
0.77
|
0.63
|
0.53
|
|
Others
|
65.80
|
66.39
|
66.38
|
0.0017
|
0.0016
|
0.0016
|
|
Total
|
100
|
100
|
100
|
160.57
|
161.96
|
167.33
|
Source: built by the
authors for (Zaitsev, 2020; Vinnichuk, 2021)
The
Herfindahl-Hirschman index of the retail services market is 160.57 in 2018,
161.96 in 2019 and 167.33 in 2020, which indicates a low market concentration.
In order to
characterize the market of retail services and establish the type of market
structure, we consider it necessary to analyse its qualitative characteristics:
the nature of services, market conditions and non-price competition (Dikan et al., 2012).
The nature of products
or services can be standardized (homogeneous), differentiated or unique. The
nature of the provision of services in the retail market can be considered
standardized, as the range of services to meet the needs of consumers of most retail businesses. Thus, today
retail enterprises provide pre-sales services (accepting orders, consulting and
informing consumers, the ability to make online orders, organizing traffic to
stores, etc.) and after-sales service (delivery of goods, packaging, lending,
etc.). At the same time, according to the results of their own
study of the activities of the fifteen largest retail enterprises in Ukraine,
they are characterized by some expansion of the range of services, i.e. there
is a tendency to differentiate.
We have identified the
following barriers to entering the retail services market:
·
Cost advantage due to longer operation of enterprises
in the market. The advantages of retailers already operating in the market
include the availability of reliable suppliers, a high level of staff skills,
customer loyalty.
·
Tendency
to product differentiation (services). Expanding the range of services, providing
unique services among competitors.
·
State regulation, which includes obtaining licenses to
trade in certain categories of goods.
In general, the
identified barriers to market entry can be described as minimal.
In the market of retail
trade services of Ukraine there is non-price competition, which is presented in
the form of creation and distribution of own trademarks (private label). The
most famous brands among retail chains are “Svoia linia”, “Vesela ferma”, “Dobryi kuhar” (LLC “ATB-MARKET”); “Semerka”,
“Saturday”, “Ukrainian Star” (LLC “Tavria-B”); “Aro”, “Fine Food” (Metro Cash & Carry Ukraine LLC); “Vyhoda”, “Varto” (PE “Varus”) and
others.
In
accordance with the identified quantitative and qualitative characteristics of
the market, as well as typical market models (Dikan
et al., 2012; Okrepky and
Mygal, 2016; Filon, 2016), we identified signs of market
concentration of retail services (Table 5).
Table 5: Signs of concentration of the
retail services market
|
Signs of market concentration
|
Market model
|
Signs of market concentration of retail
services
|
|
Pure competition
|
Monopolistic competition
|
Oligopoly
|
Monopoly
|
|
Quantitative
characteristic
|
Low level of concentration
|
Moderate level of concentration
|
High level of concentration
|
Highest level of concentration
|
Low level of concentration
|
|
Herfindahl-Hirschman index
|
ННІ < 800
|
800
< ННІ < 1800
|
НHІ > 1800
|
НHІ > 1800
|
167.33
|
|
Qualitative
features
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
The nature of the provision of services
|
Homogeneous
|
Differentiated
|
Standardized or differentiated
|
Unique
|
Homogeneous tendency to differentiation
|
|
Terms of market entry
|
No or minimal barriers to entry
|
Low barriers to entry
|
Significant barriers to entry
|
High barriers to entry
|
Low barriers to entry
|
|
Non-price competition
|
Missing
|
Considerable attention is paid to advertising and
brand creation
|
Providing advertising that emphasizes the
differentiation of products (services)
|
Image advertising, advertising
communication with public organizations
|
Considerable attention is paid to advertising and
brand creation
|
Source: Developed by the authors based on (Dikan et al., 2012; Okrepky
& Mygal, 2016; Filon, 2016)
As a
result, it can be noted that the market of retail services in terms of
quantitative and most qualitative characteristics, namely the nature of services
and market conditions, should be attributed to the market with pure
competition. There are many companies in the market; there are no trends
towards structuring.
In
general, we found an increase in retail sales, increased sales costs of
commercial enterprises, expanding the range of services of trade enterprises,
increasing the number of competitors and increasing profitability, which
indicates that the retail market is growing (Table 6).
Table 6: Life cycle analysis of the retail services market
in Ukraine
|
Criteria
|
Stages of the life cycle
|
Stages of the life cycle of
the retail services market
|
|
Entering the market
|
Growth
|
Maturity
Stability of the range of
goods / services
|
Decline
|
|
Consumers and their behaviour
|
Passive consumer behaviour
|
Increasing consumption
|
Saturation of the market,
the choice among brands becomes the rule
|
Demanding and legible consumers
|
Increasing consumption
|
|
Selling expenses
|
Highest sales costs
|
Some increase in sales
costs, but they are lower than at the market entry stage
|
Reduce sales costs
|
Low sales costs
|
Rising sales costs
|
|
Changes in goods / services
|
Narrow range of goods /
services
|
Expanding the range of goods
/ services
|
Stability of the range of
goods / services
|
Narrowing the range of goods
/ services
|
Expanding the range of goods
/ services
|
|
The nature of competition
|
A small number of
competitors
|
A large number of
competitors
|
Displacement from the market
|
Exit the market
|
A large number of
competitors
|
|
Profitability
|
Low profitability, high
prices
|
High level of profitability
|
Decrease in prices, level of
profitability
|
Lowest prices and
profitability
|
High level of profitability
|
Source: Developed by the authors based on (Porter, 2005)
The
next stage in the formation of operational strategy is the development of
marketing strategy, which for retailers, given the stage of the life cycle of
the industry, should focus on adequate planning of long-term demand and market
share by developing the sales network, expanding the range, developing its own
brand and others.
Based
on the analysis of the company's operational capabilities retail trade and their comparison of the latter
with market requirements and competitors' capabilities, an operating system for changes in consumer demand, support
for the production of quality goods under its own brand, improving service. Decisions on the choice of operational
processes, as well as the infrastructure to support them, which will achieve
certain operational priorities, may include decisions on product range
management (in particular, increasing products under its own brand), on the
organization of supply of goods and substantiation of the inventory management
system, the introduction of new services and improvement of the maintenance
process.
5.
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
The
conducted study allows us to draw conclusions:
1)
Defined in accordance with the concept of the same name, the life cycle stage
of the industry establishes the main features of the corporate strategy of the
enterprise, which in turn regulates the content of marketing and operational strategies. According to the tasks of
the marketing strategy, the operational strategy at the stage of implementation
should focus on the production of basic goods and optimization of production
costs, at the stage of growth - to ensure variability of production and yield
of improved product quality, as well as organization and improvement of
service. The operational strategy at the stage of maturity should be aimed at
creating and maintaining a sufficient variety of products, at the stage of
decline - to ensure the production of a narrow range of products under strict
control of production costs. The practical significance of the methodological approach developed by the
authors to the formation of the operational strategy of enterprises is to
create a basis for establishing its characteristics. The latter provide an
opportunity to identify the main types of management decisions made within the
operational strategy.
2) According to the
results of the life cycle analysis of the Ukrainian retail services market by
criteria: consumers and their behaviour, sales costs, changes in services, the
nature of competition and profitability, it was found that it is growing. With
this in mind, the operating strategy of retailers should be aimed at ensuring
flexibility and variability of the operating system by improving the management
of the product range, reliable organization of supply of goods and
substantiation of the inventory management system, the introduction of new
services and improvement of the maintenance process.
REFERENCES
Balabash, O., Ilin, V., Poprozman, N.,
Kuznetsova, I., Shushpanov, D., & Slavina, N. (2021). Content Strategy in Management of
Communications. Independent Journal of
Management & Production, 12(3), s232-s242. DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14807/ijmp.v12i3.1538.
Bickauske, D., Simanaviciene, Z., Jakubavicius,
A., Vilys, M., & Mykhalchyshyna,
L. (2020). Analysis and Perspectives of the Level of Enterprises Digitalization
(Lithuanian Manufacturing Sector Case). Independent
Journal of Management & Production, 11(9), 2291-2307.
Bilyavsky, V. (2015).
Technology of implementation of operational strategy of the organization. Collection of scientific works DETUT. Economics and Management Series, 34,
233-241.
Chapman, S. N.,
Arnold, J. R. T., Gatewood,
A. K., & Clive, L. M. (2017). Introduction
to Materials Management (8th ed.). Boston: Pearson
Education.
Chase, R. B., Jacobs, R. F.,
& Аkvilano, N. J. (2019). Production and operational
management, Moscow: Publishing house «Dialectic».
Dikan, V. L., Borovik, J. T., & Polyakova, O. M. (2012). Ensuring the competitiveness of
enterprises. Kharkiv: UkrDAZT.
Filon M. M. (2016).
Research of the economic essence of competition, its influence on the formation
of the market structure in the national economy. Scientific Bulletin of Kherson State University. Economic
Sciences, 17(4), 40-43. Retrieved from:
http://nbuv.gov.ua/UJRN/Nvkhdu_en_2016_17%284%29__11
Grinenko, Ju., Melnychuk, D., Mykhalchyshyna, L., Belei, S.,
& Yevtushenko, N. (2021). Improving Transfer Pricing in Ukraine using American
Experience. Independent Journal of
Management & Production, 12(3), 205-231. DOI: https://doi.org/10.14807/ijmp.v12i3.1524
Hill, T. (2005).
Operations management (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
Ishfaq, R., & Raja,
U. (2020). Empirical evaluation of IRI mitigation strategies in retail stores. Journal of the Operational Research
Society, 71, 1972-1985. DOI: 10.1080/01605682.2019.1640592.
Karpenko, L., Chunytska, I., Oliinyk, N.,
Poprozman, N., & Bezkorovaina, O. (2020). Consideration of Risk Factors in
Corporate Property Portfolio Management. Journal
of Risk and Financial Management, 13 (2), 299. DOI: 10.3390/JRFM13120299.
Karpenko, Y., Kuznetsova, I., Chykurova, A., Matveyeva, M., Hridin, O., & Nakonechna, K. (2021). Formation of the Enterprise
Strategy based on the Industry Life Cycle. Independent Journal of Management &
Production, 12(3),
262-280.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14807/ijmp.v12i3.1537
Kotsko, T.
(2016). Formation of operational strategy of energy generating enterprises of
Ukraine in the conditions of activation of threats of external environment. Economic Bulletin of the National Technical
University of Ukraine "Kyiv Polytechnic Institute", 13, 283-289.
Kuznetsova I.,
Karpenko Yu., & Vidomenko I. (2020). Technology of operational management
in the activities of port elevators. Independent Journal of Management & Production, 11(8), 762-782.
DOI: dx.doi.org/10.14807/ijmp.v11i8.1203.
Lohosha, R., Mykhalchyshyna, L., Prylutskyi, A., Kubai,
O. (2020). Institutionalization of
the agrarian market in Ukraine and European economic community: genesis,
evaluation and analysis. Independent
Journal of Management & Production, 11(8), 727-750. DOI: 10.14807/IJMP.V11I8.1232
Okrepky, R. B., & Mygal, O. F. (2016). Methodical aspects of using quantitative indicators of commodity market
concentration and the degree of its monopolization. Ukrainian Journal of Applied
Economics, 1(4), 81-88. Retrieved from:
http://dspace.wunu.edu.ua/bitstream/316497/16616/1/10.pdf.
Pisareva, N.
V. (2015). Integration of operational management tools in the management system
of agricultural enterprises, Abstract of the Dissertation, 20.
Platts, K. W., &
Gregory, M. J. (1990). Manufacturing Audit in the
process of Strategy Formulation. International
Journal of Operations and Production Management, 10(9), 5-26.
Porter, E. M.
(2005). Competitive Strategy: A Methodology for Analyzing Industries and
Competitors. Tr. from English Moscow: Alpina
Business Books, 454.
Rudnichenko, Y., Dzhereliuk, I., Mykhalchyshyna,
L., Savina, S., Pokotylova,
V., & Havlovska, N. (2020). Safe Interaction
Management of State Institutions and Business Entities Based on the Concepts of
Evolutionary Economics: Modeling and Scenario Forecasting of Processes. TEM Journal. Technology, Education,
Management, Informatics, 2, 233-241.
Santa, R. A.,
Acosta, A., Borrero, S., & Scavarda, A. (2020).
Corporate, operational, and information systems strategies: Alignment and firm
performance. Estudios Gerenciales, 157,
454-464. DOI:
10.18046/j.estger.2020.157.3749
State Statistics
Committee of Ukraine (2021). Unified State
Register of Enterprises and Organizations of Ukraine. Available:
http://www.ukrstat.gov.ua/.
Tarigan, Z. J. H., & Siagan, H. (2021). The effects of strategic planning,
purchasing strategy and strategic partnership on operational performance. Uncertain Supply Chain Management, 2,
363-372. DOI: 10.5267/j.uscm.2021.2.006.
Vinnichuk, Y. (2021). 200 largest
companies of Ukraine in 2020. Business Сensor. Available at:
https://biz.censor.net/resonance/3268870/200_nayiblshih_kompanyi_ukrani_2020_roku
Wang, M., & Huang, A. (2019). The design of a flexible capital-constrained global
supply chain by integrating operational and financial strategies. Omega-international Journal of Management
Science, 58, 40-62. DOI: 10.1016/j.omega.2018.11.016.
Zaitsev, I. (2020). Top 200: rating
of Ukrainian retailers for income, profit or loss. Retailers Association. Retrieved
from:
https://rau.ua/novyni/top-200-2/
Zalizko, V. D., Kanan, S. H., & Poprozman, N.
V. (2018). Economic and Financial Security of Azerbaijan in the Context of
Institutional Convergations. Financial and Credit Activity-Problems of Theory and Practice,
2(25), 278-287. DOI: 10.18371/FCAPTP.V2I25.136867.
Zatta, F. N., Filho, E. T., Freitas, R. R.,
Goncalves, W., Oliveira, R. R., Segura, L. C., Formigoni,
H., & Schirrmeister, R. (2021). Operational
competencies rooted in recourche theory: operations
strategy and supply chain performance. Independent
Journal of Management & Production, 12, 756-779. DOI: 10.14807/ijmp.v12i2.1161.
Zhang, Z., Zhang, S. T., & Yue, M. S. (2021). Joint pricing
and replenishment policies for risk-averse retailers under duopolistic
competition. Managerial and Decision
Economics. DOI: 10.1002/mde.3350.
 THE MAIN ASPECTS OF CHOOSING THE ENTERPRISES' OPERATING
STRATEGY
THE MAIN ASPECTS OF CHOOSING THE ENTERPRISES' OPERATING
STRATEGY